We value fostering a collaborative environment where transformative change happens. Part of that transformative change comes about when our community operates from a shared language, and a defined set of terms and words that inform our work. We are excited to share our Glossary of terms, phrases, and words that we've done our best to define.
We know this glossary is not exhaustive, and we welcome your input if you spot something that should be included!
First up, words and terms that fall in the A-B category! (click here to read all of the articles in this series)
Note: any acronyms used throughout this Glossary will be also defined alphabetically by the phrase or word’s spelling (as opposed to alphabetically by the acronym)
Accessory Dwelling Units (ADU)
A separate dwelling unit within a primary residence or a separate dwelling unit that occupies an accessory building that shares a parcel with a primary residence. As the name implies, accessory dwelling units are an accessory use to the principal use of the property.
Administration for Community Living (ACL)
An agency within the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, created to support the principle that: “All people, regardless of age or disability, should be able to live independently and participate fully in their communities, and have the right to make choices and control the decisions in and about their lives.” The ACL funds services and supports provided by networks of community-based organizations, and invests in research, education, and innovation.
Affordable Housing
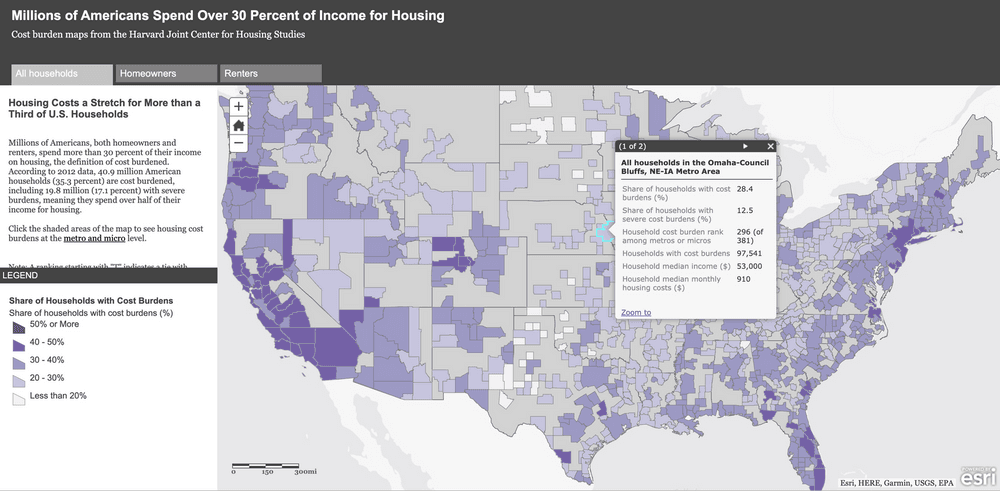
This term is often used broadly without clear definition. Under HUD rules, income-eligible households should pay no more than 30% of their gross household income for housing costs, including utilities. Some HUD Programs provide subsidies to the household or the housing development to meet the 30% rule. The 30% rule is also a benchmark for national affordability, regardless of income level. The Housing and Transportation Index (H+T Index), which provides a broader view of affordability that includes both the cost of housing and transportation combined, sets the benchmark at no more than 45% of household income.
Affordable Housing Development
An affordable housing development is housing that is specifically set aside to be below market rate so lower-income community members can afford housing without being rent burdened. Some affordable housing developments may have maximum income caps, and/or collaborate with local service providers to house those who do not currently have housing.
Affordable Housing Trust Fund (HTF)
An affordable housing production program that complements existing federal, state, and local efforts to increase and preserve the supply of decent, safe, and sanitary affordable housing for extremely low- and very low-income households, including homeless families. HTF funds may be used for the production or preservation of affordable housing through the acquisition, new construction, reconstruction, and/or rehabilitation of non-luxury housing with suitable amenities.
Aging and Disability Resource Centers
Established by the Nebraska Legislature under LB 320 in 2015 and made permanent with LB 793 in 2018 to and help elders and persons with disabilities to access services and support that help meet their long-term care needs. They partner with multiple community providers to obtain and access information and services for those seeking assistance in finding services and support.
Americans with Disabilities Act (ADA)
Federal law prohibiting discrimination against individuals with disabilities in all areas of public life, including jobs, schools, transportation, and all places open to the public. The purpose of the law is to make sure that people with disabilities have the same rights and opportunities as everyone else. ADA is commonly referenced when discussing new developments of housing, as well as when looking at preservation of existing housing stock, as there are certain requirements for the built environment that ADA provides, including housing.
Annual Homeless Assessment Report (AHAR)
HUD report to U.S. Congress providing nationwide estimates of homelessness, including information about the demographic characteristics of homeless persons, service use patterns, and the capacity to house homeless persons. The report is based on Homeless Management Information Systems (HMIS) data about persons who experience homelessness during a 12-month period, point-in-time counts of people experiencing homelessness on one day in January, and data about the inventory of shelter and housing available in a community.
Annual Performance Report (APR)
A reporting tool that HUD uses to track program progress and accomplishments and inform the Department’s competitive process for homeless assistance funding.
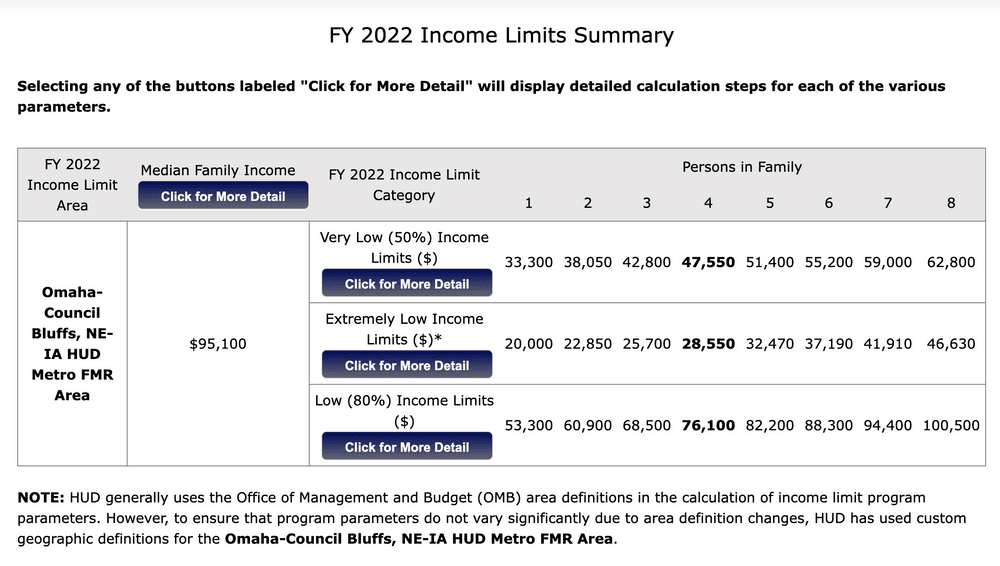
Area Median Income (AMI)
The midpoint of a county or state’s income distribution by household size, published annually by HUD. (see also the definitions for HUD Income Categories, Median, and Mixed Income Housing for more information)
Assistive Technology Partnership
A state agency in the Department of Education that provides individuals of all ages and disabilities a single point of entry to access assistive technology through exploration of potential funding sources, making equipment available for trial before purchasing, and the provision of an assessment/consultation performed by a qualified technology specialist at home, school, and work.
BIPOC
Black, Indigenous, People of Color, a term commonly used to refer to individuals who are not of European descent. (see also POC)
Blighted
An area with substantial deteriorated or deteriorating structures, defective or inadequate street layout, lots that are inadequate or inaccessible, or any other site conditions that are unsanitary or unsafe.
By Name List (BNL)
A by-name list is a comprehensive list of every person in a community experiencing homelessness, updated in real time. Using information collected and shared with their consent, each person on the list has a file that includes their name, homeless history, health, and housing needs.
~
Note: We value learning at Front Porch Investments and prioritize opportunities to continue our learning path. We will update this Glossary as we expand our awareness and seek to be as inclusive as possible! On that note, what did we miss? Email us at FrontPorch@OmahaFoundation.org to let us know what terms, words, or concepts we need to add to our Glossary!
To read the other segments of our Glossary, visit the Words Matter series.