We value fostering a collaborative environment where transformative change happens. Part of that transformative change comes about when our community operates from a shared language, and a defined set of terms and words that inform our work. We are excited to share our Glossary of terms, phrases, and words that we've done our best to define.
We know this glossary is not exhaustive, and we welcome your input if you spot something that should be included!
We've already covered the words and terms that fall in the A-H category! Read those articles
Next up, the words and terms that fall in the I-M category!
Note: any acronyms used throughout this Glossary will be also defined alphabetically by the phrase or word’s spelling (as opposed to alphabetically by the acronym).
Identity-First Language
A term that refers to someone as a disabled person instead of a person with a disability, or an autistic person, versus a person with autism. When speaking to or about individuals, always use the language they personally use and prefer (see Person First Language).
Impact Fees
Impact fees are imposed to charge the owners of newly developed properties for the "impact" the new development will have on the community. Fees can be used for such things as transportation improvements, new parks, and expansion of schools. Impact fees are not used to maintain existing facilities, but instead are used to create new facilities in proportion to the number of new developments in the area.
Inclusionary Zoning
More often in urban areas, this is a practice of planning communities and developments that will provide housing to all income brackets. Inclusionary zoning ordinances often require any new housing construction to include a set percentage of affordable housing units. The positive aspects of inclusionary zoning include the production of affordable housing at little cost to local government, the creation of income-integrated communities, and the lessening of sprawl. Negative aspects of inclusionary zoning may include shifting the cost of providing affordable housing to the private sector, and in some cases, segmenting certain income categories of its residents.
Land Trusts
Land trusts, which are trusts tied to real estate, are often used for estate planning. It is meant to be used during your lifetime for managing properties. They are revocable trusts, meaning they can be terminated or changed. Land trusts can include real estate (e.g. buildings or homes) or property notes and mortgages. They are typically used for the land involved in conservation or wildlife purposes, or for real estate development purposes. (see also Community Investment Trust and Real Estate Investment Trust)
Low Income (see HUD Income Categories)
Low-Income Housing Tax Credit (LIHTC)
A dollar-for-dollar tax credit in the United States for affordable housing investments. It gives incentives for the use of private equity in the development of affordable housing aimed at low-income Americans. Tax credits help fund the development of affordable housing, which is then rented to qualifying households. Private developers apply for the credits through a competitive points system managed by state and local allocating agencies. Since many affordable housing developers have limited use for tax credits, they often sell the credits to private investors. LIHTC is the main source of new affordable housing production—and it is needed across the region. But zoning, available land, and land costs make it difficult to create new affordable housing in areas near employment centers.
Market Rate
In the context of affordable housing, this refers to an unregulated rent that a property owner (landlord) sets or purchase price that a seller sets at whatever the market will bear. In context of interest rates, market rate is what the mortgage rate a borrower would receive in the absence of government subsidies or other programs to lower the rate.
Market Value
The sales price of a building including land cost and real estate fees.
Master Planned Community
A large-scale residential neighborhood with many recreational and commercial amenities.
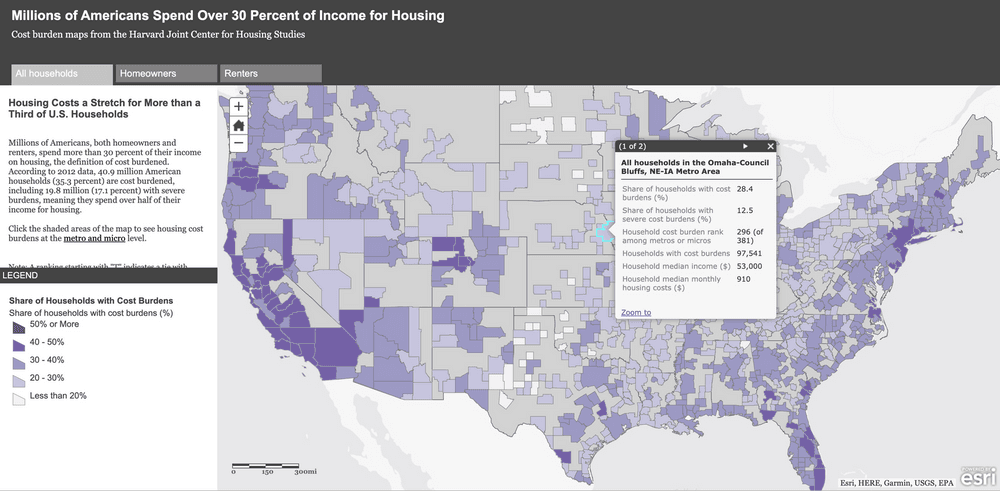
Metro Area Continuum of Care for the Homeless (MACCH)
Omaha Metro’s Continuum of Care Lead Agency. (see also Continuum of Care)
Metropolitan Statistical Areas (MSAs)
Regions that the government uses for various data-collection and budget- allocation purposes. It is the area over which HUD calculates MFI, and usually corresponds to the territory covered by a housing authority. Each MSA represents an urban core and the economically integrated surrounding area.
Missing Middle Housing
Missing Middle Housing is a range of multi-unit or clustered housing types—compatible in scale with detached single-family homes—that help meet the growing demand for walkable urban living.
Mixed Income Housing
Mixed-income housing can help to de-concentrate poverty and/or provide access to neighborhoods of opportunity for low- and moderate-income residents. This type of housing creates economic diversity and expands the availability of quality affordable housing throughout an area. Often federal, state, or local programs will define mixed income as a property in which at least 20% of the units are affordable to households making 50% AMI or less, or at least 40% of the units are affordable to households making 60% AMI or less; and at least 20% of the units are unaffordable to households making 80% AMI or less. Mixed-income housing is an important way to further residential economic diversity and federal, state, and local programs may vary depending on the market.
Multi-Family Building
A building with three or more attached units intended for living, sleeping, eating, cooking and sanitation.
~
Note: We value learning at Front Porch Investments and prioritize opportunities to continue our learning path. We will update this Glossary as we expand our awareness and seek to be as inclusive as possible! On that note, what did we miss? Email us at FrontPorch@OmahaFoundation.org to let us know what terms, words, or concepts we need to add to our Glossary!
To read the other segments of our Glossary, visit the Words Matter series.